Don’t Settle for Less: How DPDT Relays Enhance Industrial Control
In industrial automation and instrumentation control, the type of relay contacts directly affects a device’s functionality and the reliability of the control system. Two common relay contact types are Single-Pole Single-Throw (SPST) and Double-Pole Double-Throw (DPDT). These configurations differ significantly in both structure and functionality.
An SPST relay has a single set of contacts and provides simple ON/OFF control, making it suitable for basic switching tasks. In contrast, a DPDT relay contains two independent switching contact sets, allowing simultaneous control of two circuits, making it far more versatile.
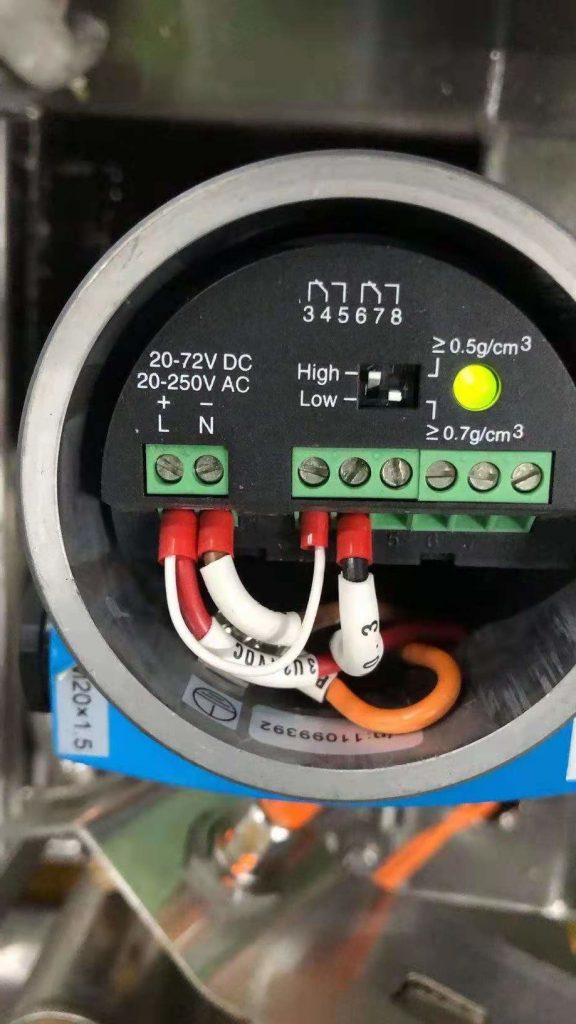

To better understand their differences, this article includes detailed wiring diagrams and real-world applications—particularly focusing on DPDT relay output in the Ring-11 tuning fork level switch.
1. SPST Relay Wiring Explained
Structure and Function
An SPST relay includes one common terminal (COM) and a single switching contact (normally open NO or normally closed NC). It controls a single circuit path—either connected or disconnected.
Wiring Diagram
Power Supply (+)
|
(COM)
O------O (NO)
|
Load (e.g., Alarm, Coil)
|
Power Supply (-)
- When the relay coil is energized, COM and NO connect, allowing current to flow.
- When de-energized, the contact opens, disconnecting the load.
Typical Applications
- Simple alarm triggering
- Basic motor start/stop control
- Cost-effective, single-signal switching
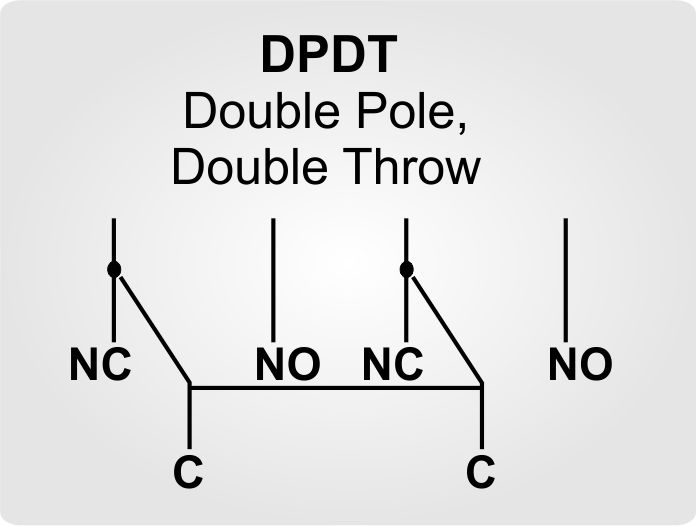
2. DPDT Relay Wiring Explained
Structure and Function
A DPDT relay consists of two completely independent SPDT contact sets. This means it has two COM terminals, each paired with an NO and NC contact. It can simultaneously control two separate circuits.
Wiring Diagram
Power Supply (+)
|
COM1 O------O NO1 ---> Load 1 (Alarm)
|
NC1
COM2 O------O NO2 ---> Load 2 (PLC Input)
|
NC2
|
Power Supply (-)
- Each contact group controls an individual circuit.
- When energized, COM1 connects to NO1, COM2 to NO2.
- When de-energized, COM1 connects to NC1, COM2 to NC2.
Typical Applications
- Dual-signal alarm systems
- Redundant output for safety-critical control
- Complex automation logic where multiple switching points are required
3. DPDT Relay Advantage: Ring-11 Level Switch Case Study
For tank-level monitoring in liquids, a DPDT-output Ring-11 tuning fork level switch offers greater control flexibility and system safety. Below is a real-world application diagram:
3.1 Wiring Scheme for Ring-11 Level Switch (DPDT Output)
Relay Output Group 1 (COM1, NO1, NC1):
- Connects to a local audio-visual alarm circuit
- Triggers warning when the liquid exceeds a preset high level
Relay Output Group 2 (COM2, NO2, NC2):
- Connects to the PLC digital input
- Sends signal to stop inflow when the tank is full, preventing overflow
This dual-loop configuration ensures that even if one system fails (alarm or PLC), the other can still operate independently, enhancing system reliability.
Wiring Diagram for DPDT Ring-11:
Power Supply +
|
COM1 O-------O NO1 ---> Alarm (Local Warning)
|
NC1
COM2 O-------O NO2 ---> PLC Digital Input (Stop Filling)
|
NC2
|
Power Supply -
In this setup, the relay coil is powered by the control circuit. Both contact sets switch simultaneously, forming a standard DPDT relay output:
- COM1 → NO1 triggers a local alarm
- COM2 → NO2 sends a signal to the PLC for automated control
- Users can configure NO or NC as per application logic
- Suitable for hygienic liquid applications—certified for IP66/IP67 and food-grade safety
4. Why Choose DPDT Output?

| Feature | SPST Relay | DPDT Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Output Channels | 1 set of contacts | 2 independent contact sets |
| Wiring Flexibility | Low | High |
| Functionality | Basic ON/OFF switching | Dual output: e.g., alarm + stop pump |
| Redundancy | None | Yes, supports backup loops |
| Recommended Use | Simple, single-signal systems | Complex logic: overflow control, alarms |
In industries like food & beverage, chemical processing, and water treatment, where liquid level control is critical, DPDT tuning fork level switches offer the flexibility and safety required.
Conclusion: Ring-11 with DPDT Relay – Reliable Level Detection
| Relay Type | Main Feature | Application Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| SPST | Single set of contacts | Cost-efficient, basic alarm or control logic |
| DPDT | Two independent SPDT contact sets | Advanced control, dual-loop redundancy |
The Ring-11 tuning fork level switch, with built-in DPDT relay output, significantly enhances compatibility and reliability for modern industrial applications.
Recommendation: For safety-critical or dual-control systems, choose a DPDT-output level switch like the Ring-11 to achieve greater flexibility, redundancy, and operational security.

