What Is a Radar Level Meter?
In modern industrial automation, liquid level measurement is a critical part of process control. As requirements for measurement accuracy, stability, and safety continue to rise, radar level meters have gradually become the preferred liquid level measuring instruments across various industries. But what exactly is a radar level meter? How does it differ from radar level sensors or radar water level meters? What applications are suitable for radar level meters? This article provides you with a thorough explanation.
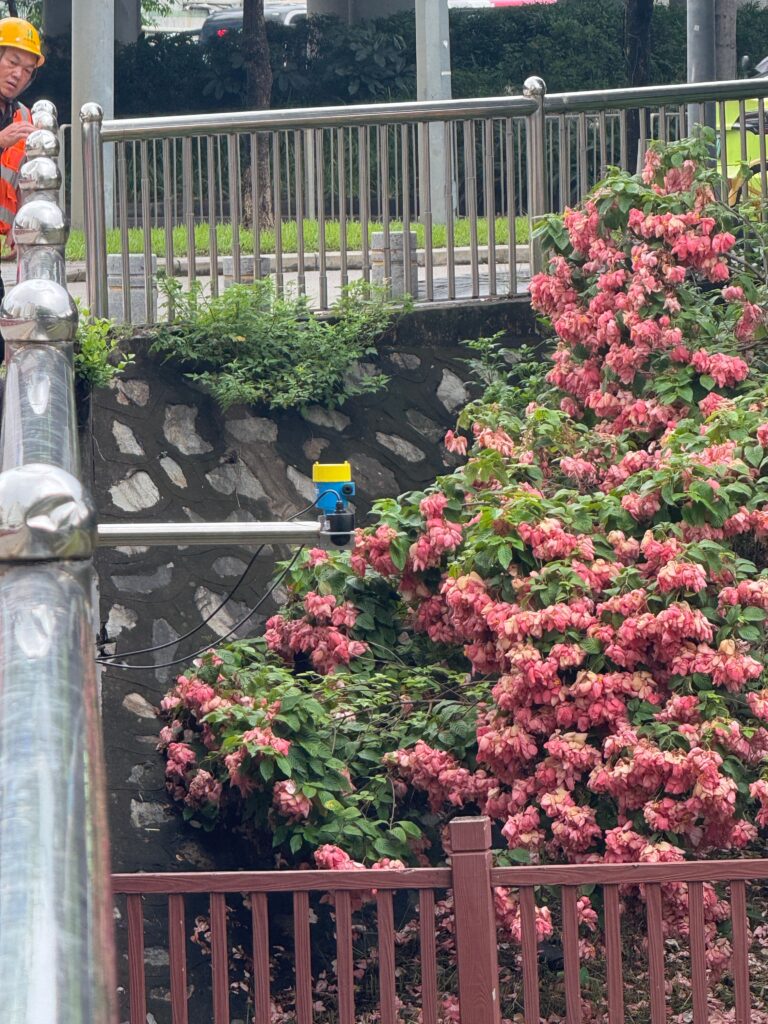

Radar Level Meter (Radar Level Gauge)
1. What Is a Radar Level Gauge?
A radar level meter is a non-contact measuring device that uses electromagnetic waves (usually microwaves) to emit and receive echo signals, enabling the measurement of liquid or solid levels. By analyzing the time difference between the emitted electromagnetic wave from the antenna and its reflection from the surface of the liquid or solid, the instrument can accurately calculate the level height. Unlike ultrasonic devices that use sound waves, radar level gauges avoid unstable factors caused by steam, dust, foam, and other complex process conditions.
Mainstream radar level gauges in the market operate mainly at 6 GHz, 26 GHz, and 80 GHz frequencies. Among these, the 80 GHz Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) radar stands out for its narrower beam angle, stronger penetration ability, and higher resolution, performing better in harsh environments. Its non-contact, wear-free, and maintenance-free characteristics ensure high reliability even in the most demanding conditions.

2. Common Synonyms and Terminology
In industry and marketing, radar level gauges are known by various names. Although the terms differ, they generally refer to the same measurement technology:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Radar Level Meter | Most commonly used term emphasizing liquid measurement. |
| Radar Level Sensor | A broader term suitable for measuring liquids, solids, and slurries. |
| Radar Water Level Meter | Used mainly in municipal water, irrigation, reservoirs, specifically for water bodies. |
| Microwave Level Meter | Emphasizes microwave technology; often an early term for radar level gauges . |
| FMCW Radar Level Meter | High-precision radar using frequency-modulated continuous wave technology. |
| High-Frequency Radar | Generally refers to 80 GHz or above radars with stronger penetration and accuracy. |
| Smart Radar Level Meter | Radar level gauges with smart algorithms, digital communication, or remote management. |
| Non-Contact Level Meter (Radar Type) | Highlights the non-contact nature, distinguishing from contact probes like capacitive or float sensors. |
Internationally, similar devices are also referred to as “Radar Level Sensor,” “Radar Level Transmitter,” or “Radar Level Gauge” in industrial procurement.
3. Working Principle of Radar Level Meters
The basic principle: the radar antenna emits a beam of electromagnetic waves towards the measured medium. When the waves reach the surface of the liquid or solid, they reflect back. The receiving antenna captures the echo and the device’s microprocessor calculates the distance by processing the time delay or frequency difference.
Common radar technologies include:
- Pulsed Radar: Emits short high-frequency pulses and calculates distance based on the time delay between emission and echo. Low power consumption and moderate interference resistance. Suitable for cost-sensitive, moderate-precision applications.
- FMCW Radar (Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave): Continuously emits electromagnetic waves with linearly varying frequency. Measures distance by analyzing the frequency difference between transmitted and received signals. Offers stronger signals, lower noise, higher accuracy, and excels in harsh conditions like high temperature, pressure, foam, and stirring.
4. Core Advantages of Radar Level Meters
- Non-contact measurement, safe and hygienic: Since radar level gauges do not touch the measured medium, issues like corrosion, blockage, or contamination are avoided. They are ideal for harsh chemicals, toxic, volatile, or flammable liquids. Hygienic radar meters comply with FDA and 3-A sanitary standards, suitable for food, pharmaceutical, and biotech industries.
- Strong interference resistance: Electromagnetic waves do not rely on air as a medium, allowing penetration through steam, mist, and foam, preventing signal distortion. This makes radar meters perfect for boilers, reactors, and sewage tanks with fluctuating process conditions.
- High precision and reliability: Mainstream 80 GHz radar meters achieve ±1 mm accuracy even with turbulent surfaces, agitation, or obstructions, accurately identifying real liquid levels and avoiding false echoes.
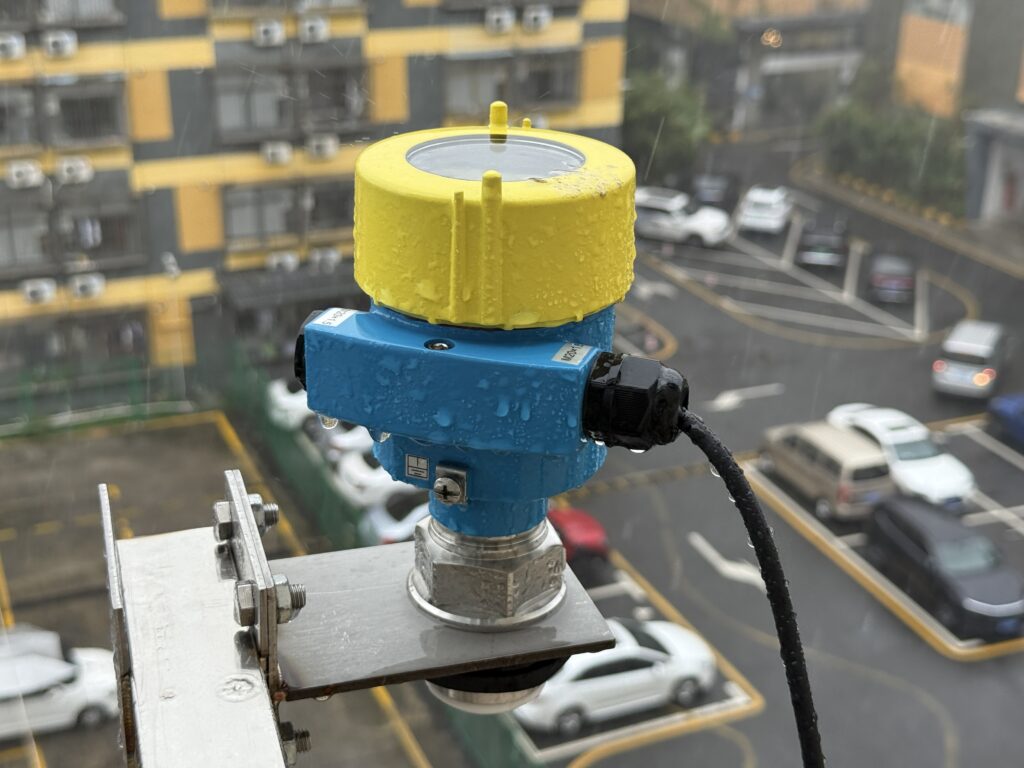

- Flexible installation and low maintenance: Narrow beam angle (~3°) easily avoids obstacles inside tanks. Fully sealed design with no moving parts ensures long maintenance intervals and reduces operational costs.
5. Broad Applications and Suitable Conditions
Radar level gauges measure liquids, slurries, solids, and foam across various industries:
| Industry | Typical Measurement Objects | Recommended Radar Type |
|---|---|---|
| Petrochemical | Storage tanks, reactors | High temperature and pressure radar |
| Power Generation | Desulfurization towers, condensate tanks, ash silos | FMCW radar level meters |
| Water Treatment | Sewage tanks, reservoirs, water tanks | Radar water level meters, smart radar |
| Grain and Feed | Silos, hoppers, high dust solids | Radar level meters with sealed antennas |
| Pharmaceutical & Food | CIP cleaning tanks, fermentation tanks | Hygienic smart radar level meters |
6. Comparison with Other Level Measurement Instruments
| Type | Contact | Accuracy | Interference Resistance | Suitable Media | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radar Level Meter | No | Within ±1 mm | Strong | Liquids, solids, slurries | Medium-High |
| Ultrasonic Level Meter | No | ±5–10 mm | Weak | Liquids (steam-free) | Medium |
| Capacitive Level Meter | Yes | ±2–5 mm | Moderate | Conductive liquids | Low |
| Magnetic Flap Level Meter | Yes | >±10 mm | Moderate | Clean, non-pressurized liquids | Low |
| Differential Pressure Transmitter | Yes | ±5 mm | Moderate | Closed tanks (requires compensation) | Medium |
Radar meters’ non-contact advantage stands out in high corrosion, fouling-prone, and sanitary environments, showing long-term superior stability compared to traditional instruments.
7. Future Trends of Radar Level Meters
Radar level meters are evolving toward higher frequency, increased intelligence, and lower power consumption:
- Intelligent and IoT integration: Next-gen radar meters will seamlessly connect with cloud platforms, MES, and SCADA systems, supporting remote monitoring, automatic diagnostics, and predictive maintenance.
- Domestic brand rise: Chinese companies like Jiwei Automations have made breakthroughs in 80 GHz radar chips, smart algorithms, and packaging, with the JWrada® series rapidly replacing costly imported products.
- Multi-function integration: Future devices may integrate temperature measurement, interface detection, foam recognition, and other functions, enhancing instrument versatility and value density.
Conclusion
Radar level meters are advanced, stable liquid level instruments that combine non-contact measurement, high accuracy, and wide applicability. They are progressively replacing traditional ultrasonic, capacitive, and float level meters as mainstream solutions. Whether called radar level meter, radar level sensor, radar water level meter, or FMCW high-frequency radar level meter, these terms reflect stages of technology development and application scope expansion.
If you seek reliable liquid level measurement solutions for complex conditions, investing in radar level meters is a wise choice.
Keywords: radar level meter, radar level sensor, radar water level meter, FMCW radar level meter, non-contact level meter, 80 GHz radar, radar liquid level measurement, smart level meter, industrial automation level instruments.
