Static Bonding for Five-Bolt Flanges: Essential Considerations in Industrial Piping Systems
In industrial pipeline design and construction, static bonding may seem like a minor detail, but it is a critical measure for electrostatic safety. This is especially true in systems conveying flammable or explosive media, where the electrical continuity of flange connections directly affects the effectiveness of static discharge prevention measures. Engineers often note: “Regardless of the number of flange bolts, if the contact resistance exceeds 0.03 Ω, bonding should be installed. Direct bonding is simpler and more cost-effective than measuring resistance for each connection.” How do international standards and industry practices address this issue?
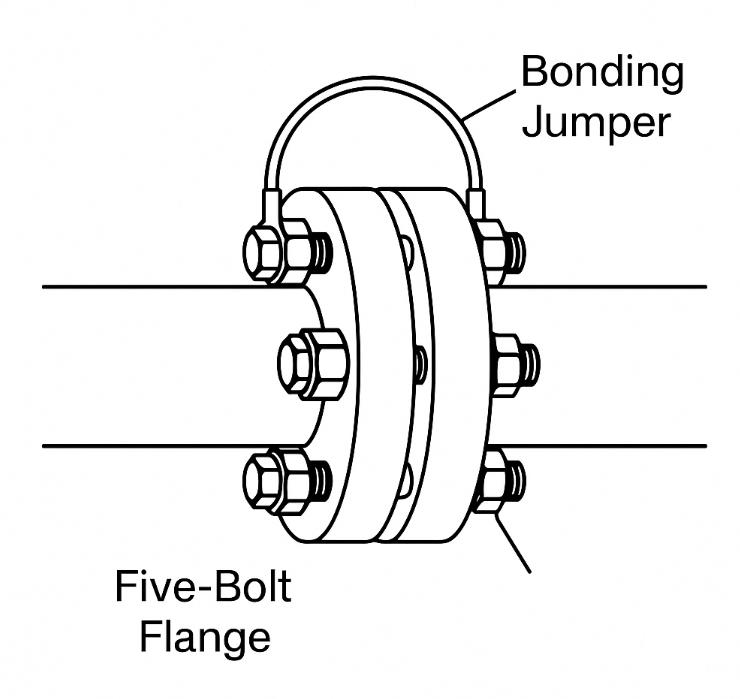
International Standards on Flange Static Bonding
While specifics may vary slightly across regions and industries, major international standards converge on the principle that high-resistance flange connections require bonding to ensure safe static discharge:
- API Recommended Practices (e.g., API RP 2003, Static Electricity Hazards in Hydrocarbon Processing)
- Metal flanges connected with conductive bolts generally maintain sufficient continuity.
- Bonding is required if measurements show high resistance or in locations with frequent corrosion.
- NFPA Standards (e.g., NFPA 77, Recommended Practice on Static Electricity)
- All conductive components in flammable or explosive atmospheres should be electrically continuous.
- Bonding across flanges is recommended if continuity cannot be guaranteed through mechanical fasteners alone.
- IEC / ATEX Guidance (IEC 60079 series)
- Equipment in explosive atmospheres must ensure equipotential bonding.
- High-resistance joints, including flanges with more than five bolts, should still be evaluated, and bonding installed if necessary.
- European Oil & Gas Engineering Practices (e.g., NORSOK R-001)
- For offshore and petrochemical pipelines, flange continuity must be verified.
- Selective bonding may be permitted in low-risk or non-corrosive conditions, but full bonding is considered safer in high-risk areas.
The common thread across standards is clear: if the resistance at a flange connection exceeds a threshold (typically around 0.03 Ω), bonding must be implemented to maintain electrical continuity.

From Standards to Practical Engineering
In practice, engineering teams adopt different strategies to ensure flange static safety:
- Full Bonding Approach
Many companies pre-install bonding wires across all flange connections, regardless of bolt count or measured resistance. This approach is common in large piping networks and explosive environments, as it provides safety redundancy and avoids the complexity of measuring resistance for each connection. - Selective Bonding
In industries such as petrochemical plants or refueling stations, selective bonding may be allowed when flange bolts number five or more and the environment is non-corrosive. In such cases, bonding is applied based on risk assessment, inspection, or periodic testing to ensure compliance.
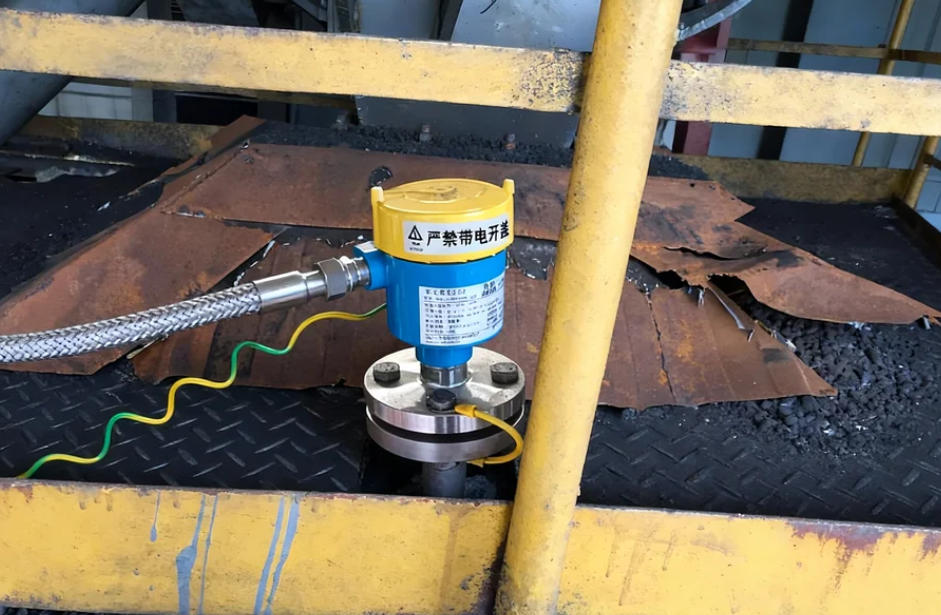

Key Considerations for Effective Bonding
Installing a bonding wire is not just “tying a copper wire.” Its effectiveness depends on installation quality, materials, and maintenance:
- Terminal Crimping and Welding
Terminals must be properly crimped or welded to flange bolts or dedicated grounding points. Loose connections or poor weld quality can lead to failure. - Conductor Selection
The bonding wire should have sufficient cross-sectional area to safely carry potential static discharge current. It should also have high conductivity and corrosion resistance to withstand harsh environments, including heat, humidity, and chemical exposure. - Corrosion Protection
In corrosive environments, terminals and wires should be plated, painted, or otherwise protected to prevent oxidation and increased resistance. - Routing and Installation
Bonding wires should be routed straight, avoiding excessive length, tangling, or mechanical stress, to maintain electrical continuity and facilitate inspection and maintenance. - Maintenance and Testing
Bonding is not a one-time measure. Flange resistance should be regularly tested using a multimeter or dedicated resistance tester to ensure it remains below the specified threshold (typically 0.03 Ω), and damaged or loose connections should be corrected promptly.
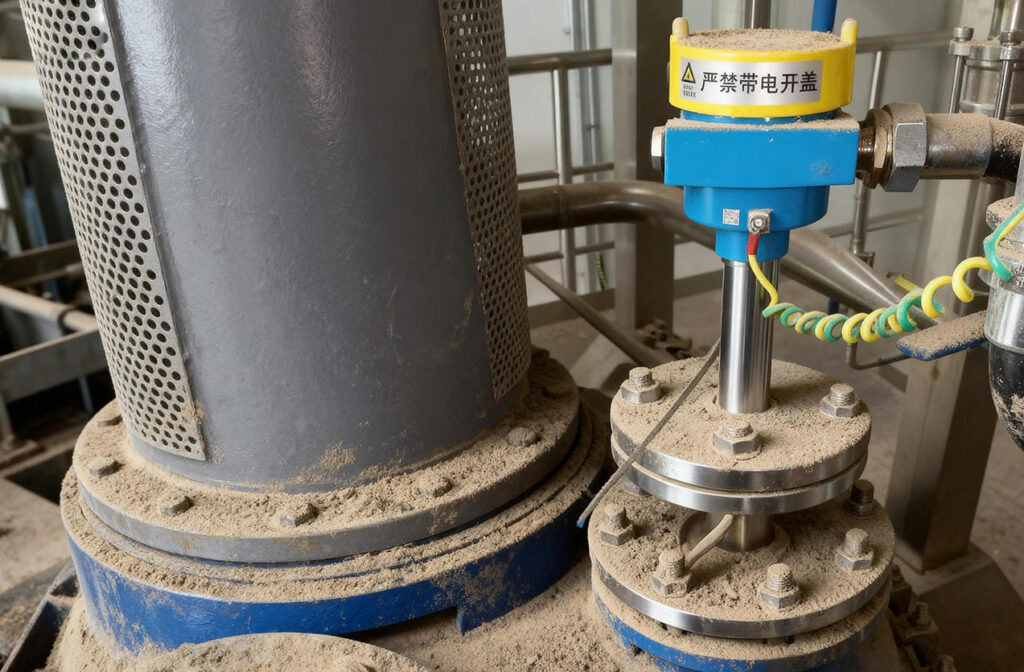

Why 0.03 Ω?
The 0.03 Ω limit is based on static charge dissipation requirements. If the resistance is too high, electrostatic charges may accumulate and create a spark hazard. A low resistance ensures nearly equal potential across the joint, minimizing the risk of spark discharge in flammable or explosive environments.
Engineering Recommendations
- Risk-Driven Approach: In hazardous areas, it is safer to over-bond than to risk unbonded connections.
- Environmental Consideration: In corrosive or high-moisture conditions, always install bonding, even if bolt count is high.
- Quality of Installation: Ensure proper crimping, welding, and corrosion protection for terminals and wires.
- Periodic Testing: Verify the electrical resistance regularly to maintain long-term safety.
Conclusion
Static bonding for flange connections, though a small step in pipeline construction, is critical for industrial safety. While international standards allow some flexibility depending on bolt count and environment, practical engineering should combine regulatory requirements with safety redundancy, installation quality, and ongoing maintenance. A simple, low-cost bonding wire can prevent potentially catastrophic incidents, making it a highly effective safety measure in flammable or explosive industrial environments.
