How Do PLCs and SCADA Work Together?
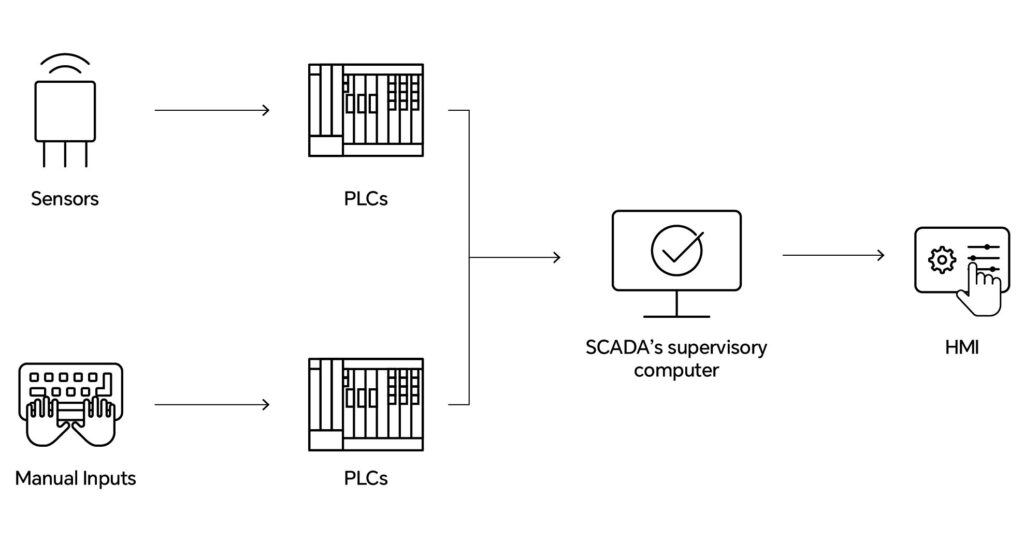
In modern industrial automation, both PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems play vital roles. Together, they control, monitor, and optimize processes across industries such as manufacturing, energy, and water treatment.
PLCs handle real-time control tasks by processing signals from field devices and sensors, while SCADA systems provide higher-level supervision, data collection, and information analysis. When combined, they form the backbone of many industrial operations, reducing the need for manual intervention, minimizing human error, ensuring safety, and enabling remote monitoring with fast, data-driven decision-making.
This article explores the details of PLCs and SCADA, including their components, programming languages, communication methods, application areas, and—most importantly—how they work together to shape the future of industrial automation.

What Is a PLC?
A PLC, or Programmable Logic Controller, is a rugged industrial computer designed to monitor sensors, gather data, and control machinery in real time.
PLCs perform specific actions when pre-programmed conditions are met. For example, they can start or stop motors, activate alarms, or adjust equipment parameters. Their resilience makes them ideal for harsh industrial environments requiring high reliability and continuous operation.
Modern PLCs have largely replaced traditional relays and timers, offering much greater flexibility, scalability, and ease of programming. As a result, they can handle everything from simple machine control to highly complex industrial processes.
What Is SCADA?
SCADA, or Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, is typically software-based and functions as the bridge between human operators and industrial equipment.
Through Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs), SCADA enables users to monitor real-time system information, send commands, and adjust settings. It integrates data from PLCs and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), creating a centralized control and visualization system for entire facilities or even geographically dispersed sites.
In short, SCADA ensures visibility and oversight, while PLCs focus on executing control logic at the equipment level.
Key Differences Between PLC and SCADA
Imagine a factory with dozens of machines. To keep everything running smoothly, you need two things: the brains (PLCs) and the supervisor (SCADA).
- PLCs are responsible for controlling machinery and ensuring tasks are executed at the right time.
- SCADA oversees the entire operation, displaying information, recording data, and allowing operators to make informed decisions.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Aspect | PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) | SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hardware device for real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes. | Software system providing visualization, monitoring, and control across facilities. |
| Components | Input/output modules, CPU, power supply. | Software, HMIs, communication servers; relies on PLC/RTU data. |
| Role | Executes control logic and manages machinery. | Provides visualization, data collection, and operator interaction. |
| Scope | Localized machine or process control. | Wide-area monitoring and centralized management. |
| Operation Speed | Real-time, high-speed control. | Real-time + historical data analysis. |
| Complexity | Implements control strategies, from simple to advanced. | Focuses on monitoring and visualization of control outputs. |
| Design | Rugged, compact hardware built for harsh conditions. | Flexible, scalable software platform installed on servers or industrial PCs. |
| Independence | Can operate standalone or within a system. | Dependent on PLC/RTU inputs for real-time data. |
| Cost-effectiveness | Affordable for machine- or line-level automation. | Higher cost, but offers broader functionality across large facilities. |
Applications of PLC and SCADA
Both PLC and SCADA systems are widely used across industries to ensure reliable control and monitoring:
- Manufacturing:
PLCs manage machinery such as robots and conveyors, while SCADA monitors production lines, allowing operators to quickly detect faults. - Energy and Utilities:
PLCs control turbines and generators, while SCADA provides a real-time overview of power generation and distribution, helping operators optimize performance. - Water and Wastewater Treatment:
PLCs control pumps, valves, and filters, while SCADA tracks flow, quality, and overall system performance, ensuring clean water supply and safe wastewater management.
Together, these systems improve efficiency, safety, and reliability across critical infrastructure.
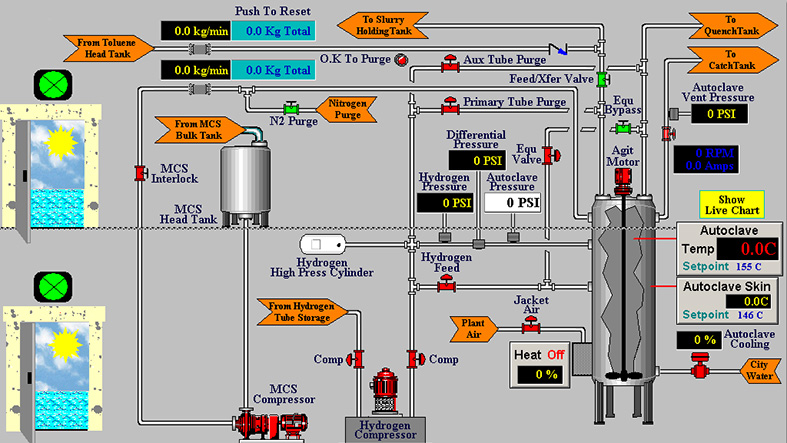
How Do PLC and SCADA Work Together?
When integrated, PLCs and SCADA systems form a complete automation ecosystem. Their collaboration is especially valuable in predictive maintenance and operational optimization.
- Sensors collect data from assets and send it to the PLC.
- The PLC processes the signals and transmits formatted data to the SCADA system.
- SCADA displays the information via HMIs, allowing operators to visualize system health.
- When thresholds are exceeded, SCADA can automatically trigger maintenance tasks or alarms.
For example, if a turbine shows abnormal vibration levels, the sensor sends data to the PLC, which forwards it to SCADA. The SCADA system then generates a maintenance work order, ensuring timely intervention.
Here, PLCs serve as data controllers and executors, while SCADA acts as the orchestrator and decision-support layer.
Integrating CMMS with SCADA and PLC
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) can be integrated with PLCs and SCADA to enhance asset monitoring and preventive maintenance.
- SCADA provides real-time insights into equipment status.
- PLCs feed detailed process data.
- CMMS uses this data to schedule, track, and optimize maintenance tasks.
By combining the three, organizations can detect issues early, diagnose faults, and ensure assets remain reliable and efficient over the long term.
FAQs
What’s the difference between PLC and SCADA?
PLCs perform real-time control of specific machines, while SCADA provides centralized monitoring, visualization, and analysis of broader processes.
Can PLC and SCADA be used together?
Yes. Integrating both improves efficiency, reduces downtime, and enables smarter decision-making.
Which industries rely on PLC and SCADA?
They are widely used in manufacturing, energy, water treatment, and utility management.
What are the future trends?
Integration with IoT, cloud-based SCADA platforms, and AI/ML for predictive analytics are shaping the next phase of automation.
How does DCS differ from SCADA?
A Distributed Control System (DCS) focuses on real-time process control within a facility, while SCADA emphasizes remote data acquisition, visualization, and wide-area supervisory control.
