White Paper on Industrial Instrument Cable Glands: Thread and Cable Matching Guide
In modern industrial automation systems, sensors and instruments are widely used for critical applications such as level measurement, pressure monitoring, temperature detection, and process control. Cable glands serve as the essential interface between instruments and external power or signal systems. Their design and selection directly impact equipment reliability, safety, and measurement accuracy. Incorrect cable gland selection may lead to unstable signals, device failures, or even safety hazards. Therefore, understanding the compatibility between cable glands and thread specifications is essential knowledge for engineers and procurement professionals.

The Role of Cable Glands in Industrial Instruments
Cable glands not only secure the cable mechanically but also provide environmental sealing, dust and water protection, and corrosion resistance.
- Mechanical Fixing: Prevents the cable from loosening or detaching under vibration or external forces.
- Environmental Protection: Maintains the instrument’s ingress protection rating (IP65/IP67), preventing dust, moisture, and corrosive media from entering.
- Safety Assurance: In high-temperature, high-pressure, corrosive, or high-dust environments, proper gland design is critical for electrical safety and measurement stability.
Proper selection of cable glands enhances instrument lifespan, reduces maintenance costs, and ensures uninterrupted production.
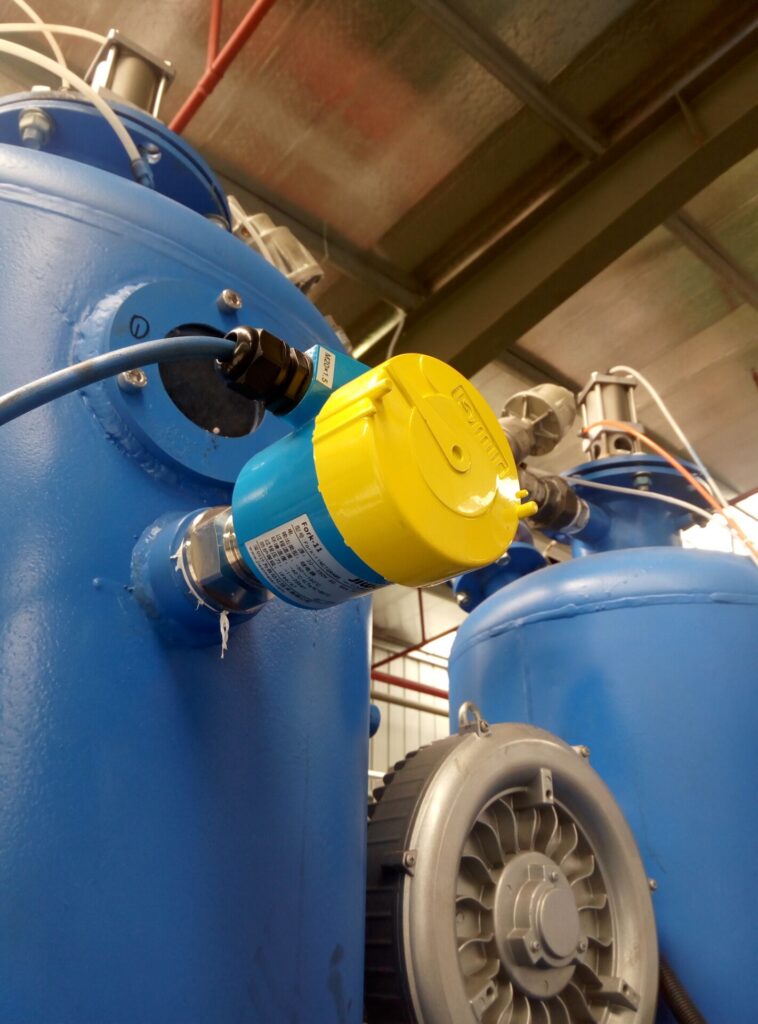

Common Cable Gland Types and Compatible Cable Diameters
1. Metric Thread (M)
Metric threads are the most common type of cable gland in industrial instruments, widely used in pressure, level, and temperature sensors.
| Thread Size | Cable Diameter | Application |
|---|---|---|
| M8×1 | 3–6 mm | Small sensors, e.g., temperature or miniature pressure sensors |
| M12×1.5 / M12×20 | 4–8 mm | Standard industrial sensors, suitable for small to medium level and pressure devices |
| M16×1.5 | 5–10 mm | Medium-sized instruments, balancing fixing and sealing performance |
| M20×1.5 | 6–12 mm | Common interface for industrial level switches and pressure transmitters |
| M25×1.5 | 8–14 mm | Large sensors or multi-core cables, ensuring stable installation |
Technical Note: When selecting metric threads, consider thread length and sealing ring configuration to ensure proper IP protection and reliable cable fixation.
2. NPT / BSPP / G Thread
NPT and BSPP threads are mainly used in North American or US-standard instruments. NPT glands are widely applied in industrial sensors, particularly for level switches and pressure transmitters.
| Thread Size | Cable Diameter | Application |
|---|---|---|
| 1/4″ NPT | 3–6 mm | Small sensors or signal cables |
| 3/8″ NPT | 4–8 mm | Small to medium instruments |
| 1/2″ NPT | 6–12 mm | Standard level switches and pressure transmitters, suitable for industrial sites |
| 3/4″ NPT | 10–16 mm | High-power sensors or multi-core cables |
Note: NPT threads usually require sealant or washers to ensure ingress protection, especially in dusty or humid environments.

3. PG Thread
PG threads are commonly used in European instruments and accommodate a wide range of cable diameters.
| Thread Size | Cable Diameter | Application |
|---|---|---|
| PG7 | 3–5 mm | Small sensor interface |
| PG9 | 4–6 mm | Industrial level or pressure switches |
| PG11 | 5–8 mm | Medium-sized devices |
| PG13.5 | 6–10 mm | Level and pressure transmitters |
| PG16 | 8–12 mm | Industrial sensors, multi-core cables |
| PG21 | 12–14 mm | Large instruments |
PG series glands are widely used in European industrial standards and can be interchanged with M20 metric threads in similar applications, provided the IP rating is considered.
Key Factors in Cable Gland Selection
- Cable Diameter Matching
Ensure the cable is securely fixed in the gland without slack, while maintaining a reliable seal. - Ingress Protection Rating
Industrial sites often require IP65/IP67; select glands according to environmental conditions. - Corrosion Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
For corrosive gases, high dust, or high-temperature environments, use stainless steel or high-temperature resistant plastic glands with corrosion-resistant sealing rings. - Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Thread size should allow convenient field operation, minimizing installation and maintenance time.

Case Study
For industrial level switches with a cable diameter of 6–12 mm:
- Metric Option: M20×1.5
- European Option: PG16
- US Standard Option: 1/2″ NPT
M20×1.5 or PG16 ensures secure fixation and sealing, suitable for most level and pressure sensors. The 1/2″ NPT thread is more suitable for thicker or multi-core cables but requires additional sealing measures.
Conclusion
Scientific selection of cable glands is crucial for ensuring long-term stable operation of industrial instruments. Understanding the compatibility between metric, NPT, US-standard, and PG threads and their corresponding cable diameters, combined with ingress protection, corrosion resistance, and installation requirements, can significantly enhance equipment reliability and reduce failure risks.
Through the system comparison and case study presented in this white paper, engineers can quickly determine the most suitable cable gland type, achieving efficient, safe, and reliable instrument installation and maintenance.
