SIL Failure Rate Requirements: Understanding Safety Integrity Level Standards for Industrial Instrumentation
SIL Failure Rate Requirements are essential benchmarks defined by international standards to guarantee the reliability and safety of Safety Instrumented Systems (SIS) used in industrial processes. SIL, or Safety Integrity Level, quantifies the ability of safety instruments and systems to perform their intended safety functions without failure, especially in hazardous conditions. Proper understanding and implementation of these failure rate requirements ensure that safety devices effectively prevent accidents and protect personnel, equipment, and the environment.
What is SIL and Why SIL Failure Rate Matters
Safety Integrity Level (SIL) is a measure of the relative risk reduction provided by a safety function. The concept is standardized mainly through IEC 61508 and IEC 61511 — the fundamental international standards governing functional safety and safety instrumented systems in process industries.
The failure rate requirement of a device directly impacts its assigned SIL level. Failure rate is typically expressed as the number of failures per hour (λ), calculated as the reciprocal of the Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF). A lower failure rate corresponds to higher reliability and thus a higher SIL level.

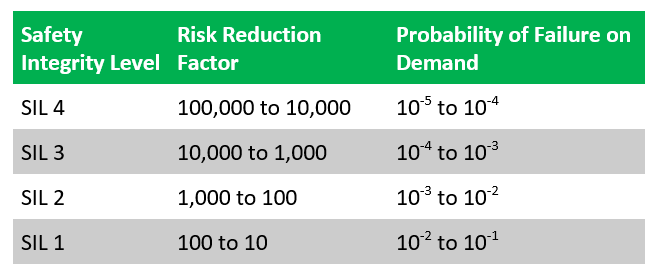
SIL Levels and SIL Failure Rate Ranges
SIL is classified into four levels: SIL 1 to SIL 4, with SIL 4 being the most stringent. Each level has specific failure rate requirements defined as:
- SIL 1: Failure rate between 10^-5 and 10^-4 failures per hour, suitable for basic safety functions.
- SIL 2: Failure rate between 10^-6 and 10^-5 failures per hour, for moderate risk reduction.
- SIL 3: Failure rate between 10^-7 and 10^-6 failures per hour, for high-risk environments.
- SIL 4: Failure rate between 10^-8 and 10^-7 failures per hour, the highest safety level, often used in nuclear or extremely hazardous applications.
For example, Jiwei’s Ring-11 tuning fork level switches and magnetic flap level meters have achieved SIL 2 and SIL 3 certification levels, meeting stringent failure rate standards for reliable performance in demanding industrial environments.

Standards Guiding SIL Failure Rate Requirements
IEC 61508 provides the overarching framework for functional safety, applicable to a broad range of industries. It defines methodologies for determining failure rates, safety lifecycle management, and validation processes to ensure systems meet the required SIL levels.
IEC 61511 focuses specifically on safety instrumented systems in process industries such as chemical plants, refineries, and oil & gas facilities. This standard guides how SIL levels should be selected based on hazard and risk assessments, emphasizing practical implementation of safety functions.

Calculating and Evaluating SIL Failure Rates
Achieving the required SIL failure rate involves several analytical tools and design approaches:
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA): Identifies and evaluates potential failure modes in safety instruments, estimating their impact on system safety and reliability.
- Fault Tree Analysis (FTA): Uses logical diagrams to map how different component failures can combine to cause hazardous system failures, facilitating risk mitigation.
- Redundancy and Diversity: Systems designed with redundant components or diverse technologies reduce the likelihood that a single failure leads to system loss of safety function. Dual or triple redundancy is common in SIL 3 or SIL 4 applications.
Importance of SIL Certification and Authenticity
SIL certification must be validated by independent third-party bodies to ensure compliance with IEC 61508 and IEC 61511. Authentic certification confirms that instruments meet failure rate targets and performance criteria necessary for safe operation.
Users are encouraged to verify SIL certificates through official national accreditation websites such as the CNCA in China. This step prevents the use of counterfeit or unqualified safety instruments, which can jeopardize safety and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
SIL failure rate requirements play a critical role in guaranteeing the safety and reliability of industrial instrumentation and safety systems. By adhering to IEC 61508 and IEC 61511 standards, manufacturers and users can design, select, and maintain safety instruments that effectively minimize risks in hazardous environments.
Selecting SIL-certified instruments like Jiwei’s tuning fork level switches and magnetic flap level meters ensures compliance with rigorous failure rate criteria, providing confidence in the integrity of safety instrumented systems.
