Radar Antennas: Key Components and Applications
Radar antennas are essential components in radar systems, responsible for transmitting and receiving electromagnetic wave signals. Depending on their structure, emission methods, and application fields, radar antennas can be classified into various types. Each type has specific advantages and applications. Below is a classification of common radar antennas and their characteristics.
1. Classification by Structural Form
1.1 Parabolic Antenna
- Structure: Parabolic antennas typically consist of a reflective surface (shaped like a bowl) and a feed located at the focal point. The working principle involves focusing the electromagnetic waves emitted from the feed into one direction using the reflective surface.
- Advantages: High gain, focused beam, ideal for long-distance detection. Due to its high-gain properties, it is commonly used in long-range target tracking, such as weather radar, satellite communication, and marine radar systems.
- Applications: Large-scale meteorological observation, deep space communication, satellite communication, long-range radar systems.
1.2 Horn Antenna
- Structure: The horn antenna has a shape similar to an expanded horn, typically consisting of a metal waveguide and a horn-shaped opening. It functions to transmit electromagnetic waves from the waveguide into the air, creating a relatively uniform beam.
- Advantages: High operating frequency, small standing wave, strong directivity. Its simple structure and wide frequency bandwidth make it suitable for high-frequency radar systems, particularly for microwave applications.
- Applications: Meteorological radar, aircraft radar, satellite communication, microwave measurement systems.
1.3 Microstrip Antenna (Patch Antenna)
- Structure: A microstrip antenna is a flat-panel antenna typically embedded in a printed circuit board with conductive metal patches. It is widely used in high-frequency electronic devices. Its small size makes it ideal for integration.
- Advantages: Small size, high integration, low manufacturing cost. Its flat design allows for high integration, making it especially suitable for portable devices.
- Applications: Portable radar systems, car-mounted radar, drone radar, miniature radar sensors.
1.4 Slot Antenna
- Structure: Slot antennas typically consist of slits on a metal plate, where the shape and size of the slits determine their radiation characteristics. The principle involves generating radiation when current flows through the slits.
- Advantages: Strong directionality and high gain, suitable for long-distance signal transmission or reception. They can effectively focus the signal, making them ideal for applications requiring high directivity.
- Applications: Shipboard radar, aircraft radar, satellite communication, communication devices.
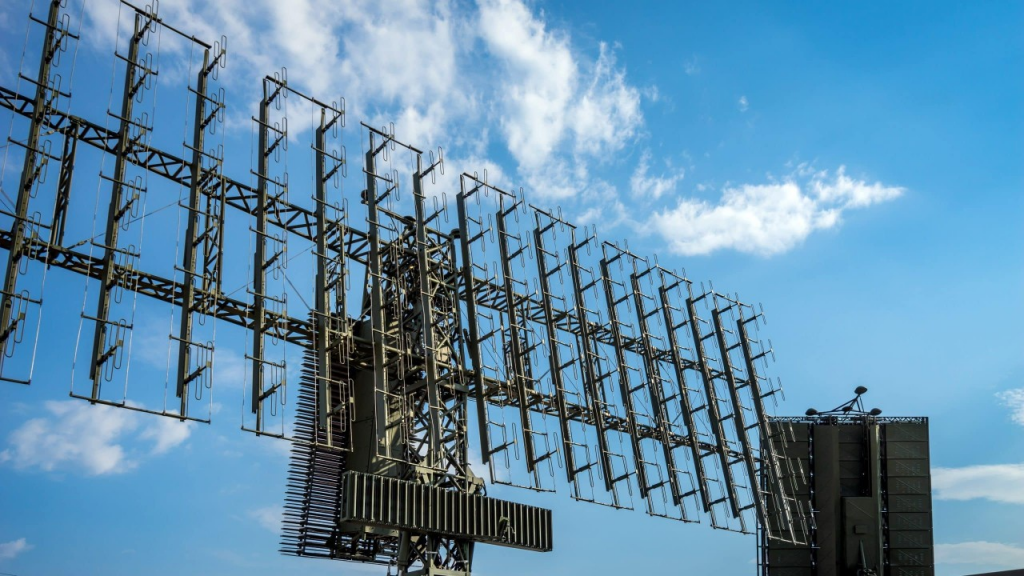
1.5 Planar Array Antenna
- Structure: Composed of multiple small antenna elements arranged in a planar array, the beam direction can be controlled electronically by adjusting the phase of each unit.
- Advantages: Allows fast electronic scanning with high directivity and flexibility. Commonly used in phased array radar, ideal for fast response and high-precision applications.
- Applications: Modern military radar, aircraft radar, satellite communication systems, advanced meteorological radar.
2. Classification by Beam Control Method
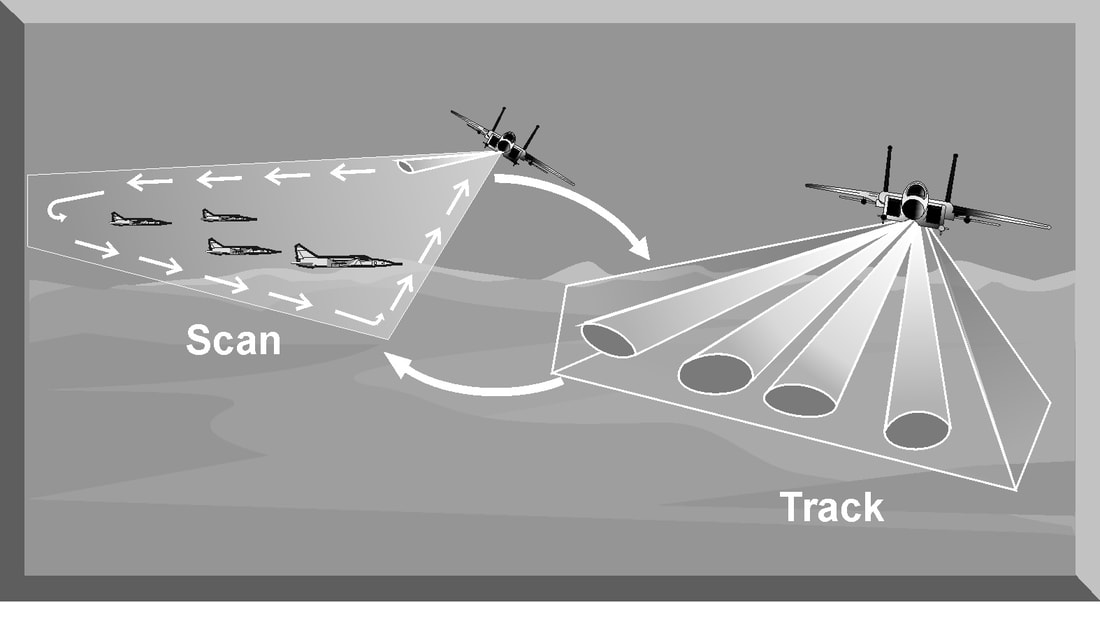
2.1 Mechanical Scanning Antenna
- Structure: Mechanical scanning antennas change the direction of the beam by physically rotating or tilting the antenna.
- Advantages: Simple design, low cost, commonly used in traditional radar systems for applications requiring periodic scanning.
- Applications: Meteorological radar, marine radar, airport surveillance radar.
2.2 Electronic Scanning Antenna (Phased Array Antenna)
- Structure: The beam direction is controlled by adjusting the phase of each antenna unit electronically, without the need for physical rotation, enabling fast electronic scanning.
- Advantages: Fast beam control, high accuracy, no mechanical components, reducing maintenance costs. It is ideal for rapid response, especially in complex environments.
- Applications: Modern military radar, high-end meteorological radar, airborne radar, space communication.
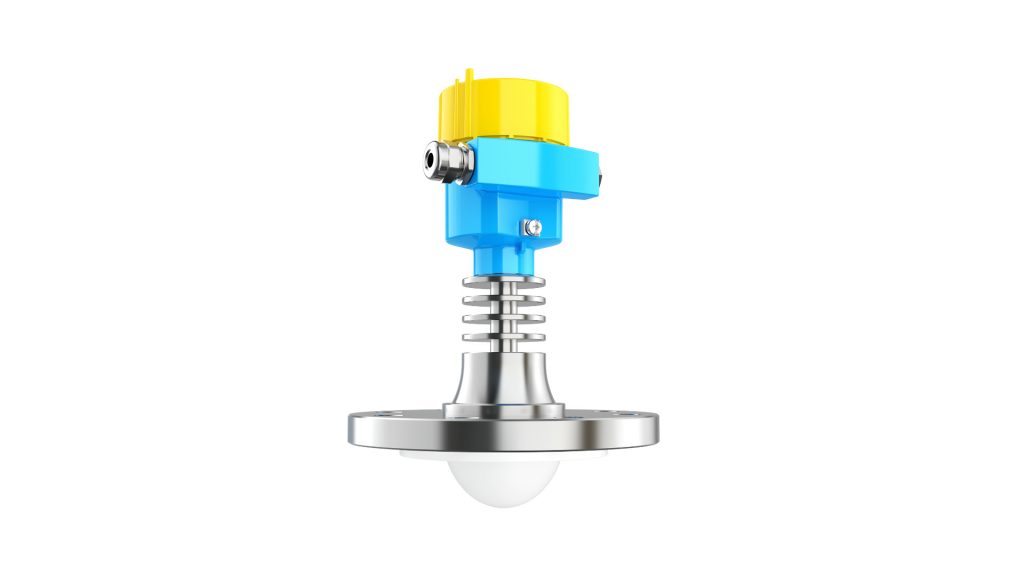
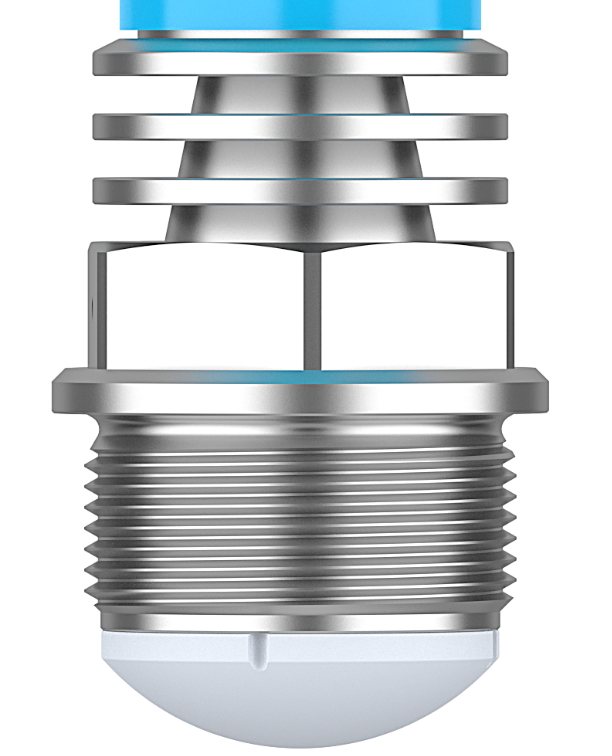
3. Radar Antenna Types in Level Measurement
In industrial applications, radar level meters are widely used for measuring both liquids and solids, especially in industries such as petrochemicals, food, and pharmaceuticals. Depending on the working environment and measurement needs, there are various antenna types for radar level meters:
3.1 Horn Type Antenna
- Applications: Commonly used in 26GHz or 80GHz radar level meters for measuring most liquids or solid materials. Due to its high-frequency characteristics, it allows for precise level measurement.
- Characteristics: High frequency bandwidth, ideal for most liquid and powder material measurement scenarios.
3.2 Parabolic Type Antenna
- Applications: Suitable for measuring long distances and scattering materials such as coal, cement, and other solids.
- Characteristics: Excellent long-range detection ability and directionality, ideal for large-scale level measurement, effectively avoiding environmental interference.
3.3 Lens Type Antenna
- Applications: Primarily used in high-frequency radar (such as 80GHz radar), it can generate a narrow beam, making it suitable for environments with limited space.
- Characteristics: Narrow beam, high-precision measurement, ideal for small spaces or environments with high interference, such as confined tanks.
3.4 Array Type Antenna
- Applications: High integration, compact size, commonly used in compact radar level meters. It can flexibly control the beam and is suitable for complex working conditions.
- Characteristics: High flexibility, ideal for small devices or narrow spaces, capable of quickly adjusting the beam direction.

4. Application Cases
- Meteorological Radar Antenna: Uses parabolic antennas to efficiently detect weather phenomena like storms and precipitation, providing comprehensive weather data for forecasting and disaster warning.
- Marine Radar Antenna: Employs horn antennas to assist in navigation and collision avoidance, especially under harsh sea conditions, providing crucial safety guarantees.
- Military Radar Antenna: Uses phased array antennas for rapid target scanning and locking, widely applied in missile defense, fighter radar, and naval ship monitoring systems.
- Industrial Radar Antenna: In level measurement, lens and horn antennas are used in oil, gas, chemical, and food industries to monitor liquid and solid levels, providing real-time data for critical processes.
Conclusion
Radar antennas, as core components of radar systems, come in various types and offer broad applications. With the advancement of technology, radar antennas are becoming increasingly prevalent in industries such as defense, meteorology, and manufacturing. When choosing the appropriate antenna, it is important to consider factors such as frequency, beam directionality, and environmental adaptability to ensure optimal radar system performance.

