Why 120-Ohm Termination Resistors Are Essential in RS-485 Communication Systems
RS-485 communication is widely adopted across industrial control, security surveillance, and smart device applications due to its robust noise immunity, long-distance transmission capabilities, and support for multi-point communication. However, during the commissioning and troubleshooting phase, many engineers often encounter a recurring issue: Why is it necessary to install 120-ohm termination resistors at both ends of the RS-485 bus?
In this article, we’ll explore the role and importance of termination resistors, focusing on their application in industrial instrumentation and real-world environments.
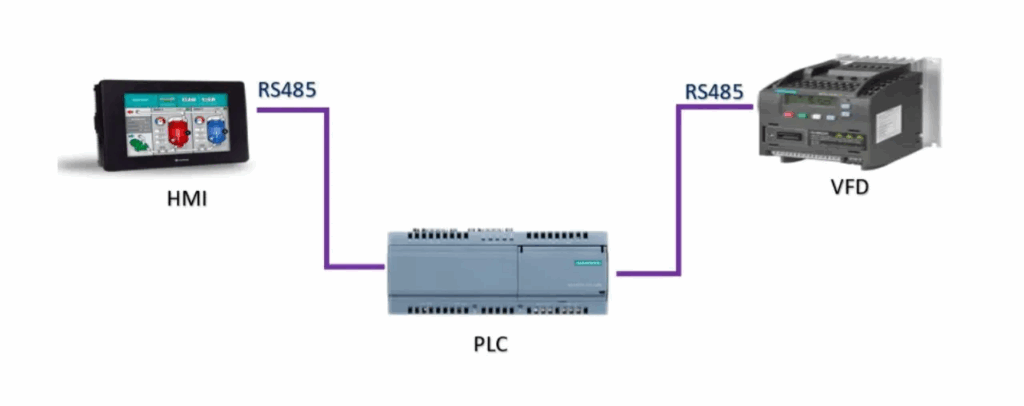
Introduction to RS-485 Communication
RS-485 is a differential communication standard designed for reliable data exchange in harsh environments. Its key advantages include:
- Strong Noise Immunity: Differential signaling helps suppress common-mode electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Long Transmission Distance: RS-485 can transmit data over distances up to 1200 meters.
- Multi-Device Support: It allows up to 32 nodes to communicate over the same bus.
In most real-world applications, the RS-485 network is wired in a bus topology. To ensure signal integrity, proper impedance matching at both ends of the bus is crucial, which is where termination resistors come into play.
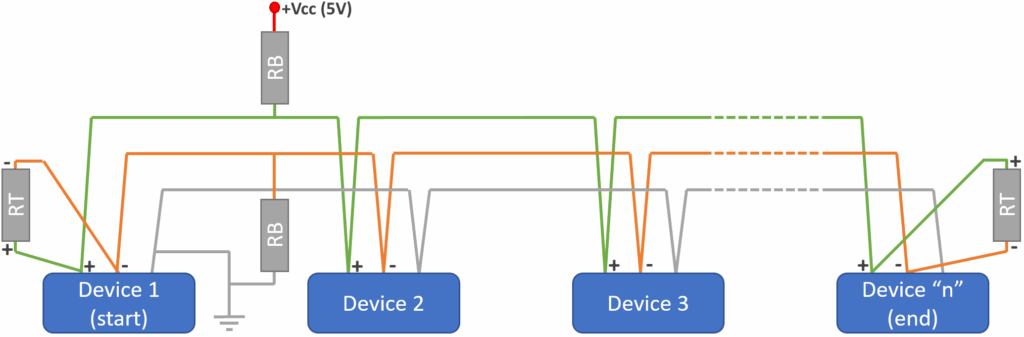
Why Termination Resistors Are Not Optional
Termination resistors are not just a best practice—they are a requirement for maintaining reliable communication, especially in systems with long cables or high data rates. Here’s why they matter:
1. Preventing Signal Reflection
When a digital signal reaches the end of a transmission line and encounters an impedance mismatch, it gets reflected back along the cable. These reflected signals can interfere with incoming data, resulting in distorted waveforms and communication errors. Termination resistors absorb these signals and prevent reflections from occurring.
2. Ensuring Impedance Matching
Most RS-485 cables have a characteristic impedance of around 120 ohms. By placing a 120-ohm resistor at each end of the bus, the system matches this impedance, enabling clean signal transmission and minimizing energy loss or bounce-back.
3. Maintaining Signal Integrity
Without proper termination, reflected signals can superimpose on valid data, causing voltage spikes or false transitions. This is especially problematic during high-speed or long-distance transmissions, where small errors can propagate and disrupt entire communication chains.
Why Specifically 120 Ohms?
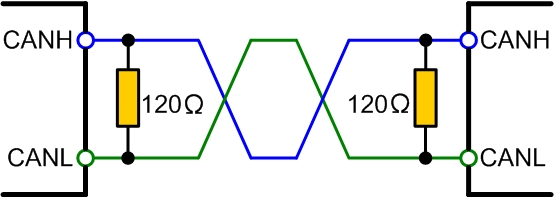
The 120-ohm value isn’t arbitrary—it matches the characteristic impedance of standard twisted-pair RS-485 cables. Here’s what happens when mismatched resistors are used:
- Too High: Signals are inadequately absorbed and reflections persist, degrading communication quality.
- Too Low: The signal strength drops excessively, reducing the communication range.
Through years of practical implementation, 120 ohms has proven to be the optimal value to balance energy absorption and signal clarity.
Best Practices for Implementing Termination Resistors
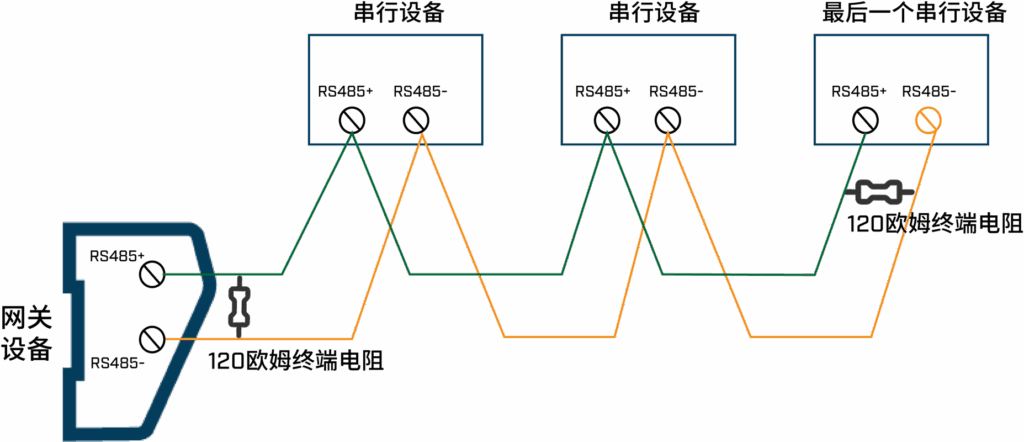
1. Placement Matters
Termination resistors should only be placed at the two physical ends of the RS-485 bus. Intermediate nodes should not have termination, as adding more resistors can unbalance the system and increase signal loss.
2. Resistor Selection
A 120-ohm, ¼-watt metal film resistor is generally sufficient for most industrial environments. While some short-distance setups (less than a few meters) might work without termination, it’s still recommended for high-speed communication to ensure long-term stability.
Real-World Case Study: RS-485 in a Chemical Plant
A chemical processing plant implemented RS-485 to connect multiple field sensors across long distances. Initially, the system operated without termination resistors. Over time, the communication became increasingly unstable—data packets were lost, alarms were triggered, and sensor readings were delayed. As more nodes were added, these problems intensified.
Upon installing 120-ohm termination resistors at both ends of the RS-485 bus, the signal reflections disappeared. Communication became stable, and system reliability improved significantly. This case highlights how a small, inexpensive resistor can make a substantial difference in data integrity.
Common Misconceptions
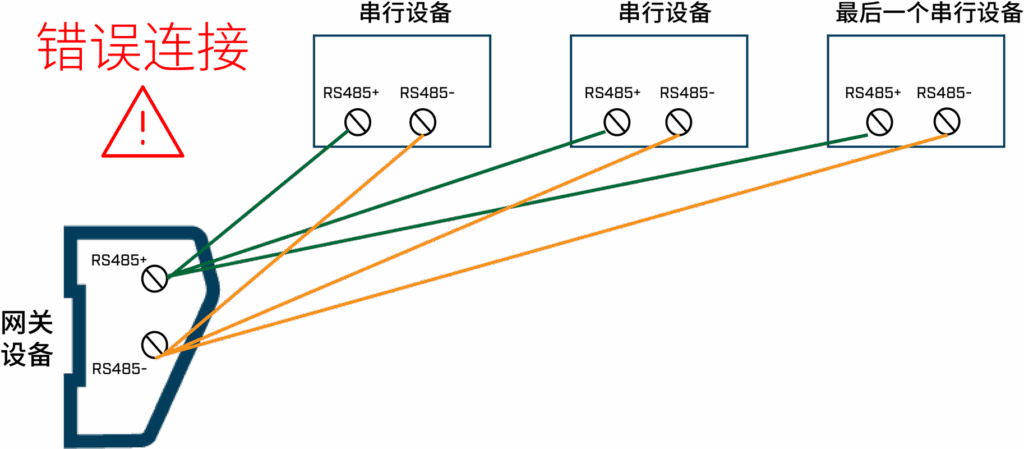
Let’s clear up some frequent misunderstandings around RS-485 termination:
- Myth 1: Every node needs a resistor
Reality: Only the two end devices should have termination resistors. Adding more can disrupt the impedance balance. - Myth 2: Termination isn’t needed for short distances
Reality: While short cables may function without termination under ideal conditions, electromagnetic noise or high-speed transmission still warrant proper termination. - Myth 3: Any resistor value will do
Reality: The resistor value must match the cable’s characteristic impedance—120 ohms is the standard and most effective choice.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
Though small in size and often overlooked, termination resistors are critical for ensuring stable and reliable RS-485 communication. Especially in systems involving long-distance wiring, high data rates, or multiple nodes, proper termination can significantly reduce communication errors and downtime.
For any RS-485-based instrumentation or control system, always adhere to the following best practices:
- Install 120-ohm termination resistors at both ends of the bus.
- Use high-quality resistors with stable temperature coefficients.
- Review the physical topology of your network to confirm proper placement.
By paying attention to this seemingly minor detail, engineers can prevent major issues and ensure smooth communication across the entire system.
